CPM/cz5108
Closest Point Method. Chen, Wathen and Zhu
| Name |
cz5108 |
| Group |
CPM |
| Matrix ID |
2564 |
|
Num Rows
|
5,108 |
|
Num Cols
|
5,108 |
|
Nonzeros
|
51,412 |
|
Pattern Entries
|
51,412 |
|
Kind
|
2D/3D Problem |
|
Symmetric
|
No |
|
Date
|
2012 |
|
Author
|
Y. Chen, A. Wathen, S. Zhu |
|
Editor
|
T. Davis |
| Structural Rank |
5,108 |
| Structural Rank Full |
true |
|
Num Dmperm Blocks
|
2 |
|
Strongly Connect Components
|
2 |
|
Num Explicit Zeros
|
0 |
|
Pattern Symmetry
|
43.4% |
|
Numeric Symmetry
|
23.6% |
|
Cholesky Candidate
|
no |
|
Positive Definite
|
no |
|
Type
|
real |
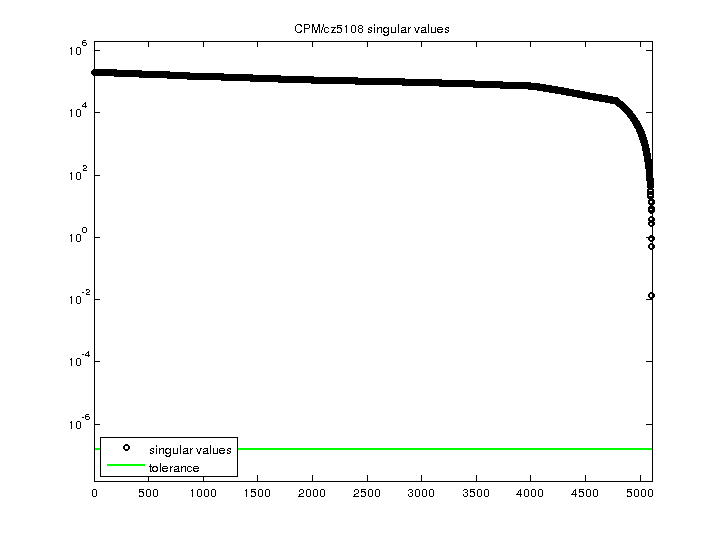
| SVD Statistics |
| Matrix Norm |
2.023395e+05 |
| Minimum Singular Value |
1.397018e-02 |
| Condition Number |
1.448367e+07
|
| Rank |
5,108 |
| sprank(A)-rank(A) |
0 |
| Null Space Dimension |
0 |
| Full Numerical Rank? |
yes |
| Download Singular Values |
MATLAB
|
| Download |
MATLAB
Rutherford Boeing
Matrix Market
|
| Notes |
Closest Point Method, Yujia Chen, Andy Wathen, Shengxin Zhu
A method for computing on surfaces. For more information see:
http://people.maths.ox.ac.uk/~macdonald/closestpoint/
One of the matrices in this collection (cz10228) is solved poorly
by x=A\b in MATLAB R2012a. The solution is to use this setting:
spparms ('piv_tol', 0.5)
x = A\b
which changes the pivot tolerance. MATLAB has a test which
checks the accuracy of x=A\b when using UMFPACK, and if the
accuracy is poor, it refactorizes the matrix with a piv_tol
of 1.0 (standard partial pivoting). For the cz10228 matrix,
the test is nearly, but not quite, triggered. The other matrices
do not cause this problem.
Further details from Shengxin Zhu:
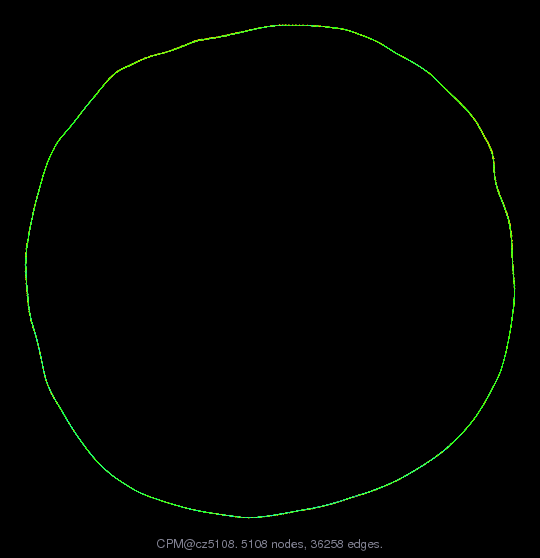
Generally speaking, the matrix comes from the numerical solution of
Poisson equation on a unit circle by solving an embedding PDE posed
in a narrow band around the circle. Of course the easiest way to
solve PDE on a unit circle is to parametrize it and then solve a 1D
problem; but here we just want to test the effectiveness of the
embedding method for solving PDEs on general curves or surfaces.
The method extends the original surface PDE to a band around the
surface, and then solve the extended PDE on a Cartesian grid by a
finite difference scheme. In order to define such a PDE, one has to
both define proper embedding differential operator and extend the
solution from the surface to the embedding space. One natural way
is to enforce the solution being constant along the normal
direction of the surface so that the surface differential operator
could be replaced by standard Cartesian differential operator. Here
in the case of Poisson equation on a unit circle, we solve a
standard Poisson equation on a 2D cartesian grid around the circle
with suitable right hand side and Neumann boundary condition on the
boundary of the band. We enforce the Neumann boundary condition by
taking the value of each boundary point to be the value of its
closest point on the circle; and since the closest point is usually
not a grid point, its value is obtained by interpolation of values
of the surrounding points. Putting the process into a sparse
matrix, and change one row of the matrix to fix the value of one
point of the solution and ensure the matrix is nonsingular.
I tried different bandwidth, different interpolation order for the
value of the closest points, 2nd order and 4-th order finite
difference scheme to the Laplace operator. In most cases, MATLAB
backslash works pretty well in solving the resulting linear system.
The size of the matrix which makes MATLAB backslash not work is not
the largest among all, and its condition number is not largest
among all. By the way, the AMG solver by Notay and a geometric
multigrid solver written by myself works pretty well for this case.
|